相关性搜索(searching with relevancy)时,返回结果添加score.用以反应搜索结果与搜索语句的相关程度。
Elasticsearch中打分机制的工作原理
决定查询和返回结果相关程度的过程就称之为打分。
怎样实现文档打分
在单一文档中term出现的频率TF越高,相关度越高,也就是score越高。term跨所有文档出现的频率越高,相关度越低,score也就越低。
term 频率 (term frequency TF)
搜索时,term在文档中出现的频率。比如搜索elasticsearch
A.“We will discuss
Elasticsearchat the next Big Data group.”
B.“Tuesday the
Elasticsearchteam will gather to answer questions aboutElasticsearch.”
A中TF就是1,B中TF就是2。那么B的打分就高。
文档反向索引频率(Inverse document frequency IDF)
term索引的文档的数量。
示例文档:
A: “We use
Elasticsearchto powerthesearch for our website.”
B: “
Thedevelopers likeElasticsearchso far.”
C: “
Thescoring of documents is calculated bythescoring formula.”
Elasticsearch 的文档频率(DF)是2. the的文档频率是3.
就是利用TF和IDF计算文档的得分。
Lucene的打分公式
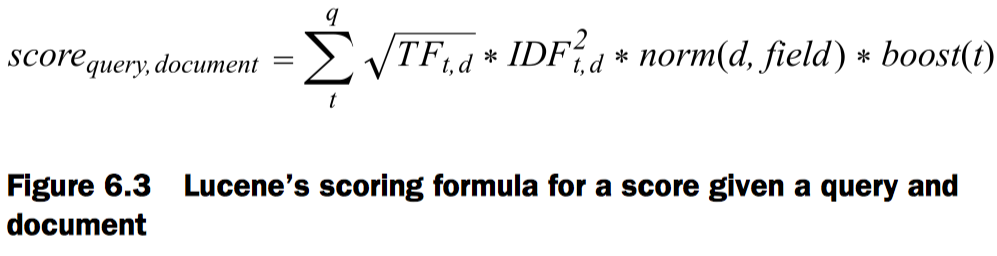
其他打分方法
主要介绍:Okapi BM25,配置方法有两种。 一种是在字段mapping时,
{
"mappings": {
"get-together": {
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "string",
"similarity": "BM25" //设置打分方法为BM25
}
}
}
}
}
另一种作为全局使用:
配置elasticsearch.yml设置默认打分方法为BM25
index.similarity.default.type: BM25
Boosting
两种不同的boosting类型
- 索引数据时(改变boosting需要重新索引数据)
- 查询文档时(改变boosting无需重新索引数据)
推荐使用文档查询时,因为其灵活。使用boosting修改字段的打分权重。
索引时boosting
简要介绍(一般不推荐使用)。示例:
curl -XPUT 'localhost:9200/get-together' -d '{
"mappings": {
"group": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"boost": 2.0,
"type": "string"
},
...rest of the mappings...
}
}
}
}'
缺点就是改变boost值需要重新索引数据
查询时boosting
配置boost示例:
curl - XPOST 'localhost:9200/get-together/_search?pretty' - d '{
"query": {
"bool": {
"should": [{
"match": {
//Query - time boosting of this match query
"description": {
"query": "elasticsearch big data",
"boost": 2.5
}
}
}, {
"match": {
//No boosting for the second match query
"name": {
"query": "elasticsearch big data"
}
}
}]
}
}
}'
字段description配置boost,字段name没有配置该参数,意味着description对查询结果有更大的影响力。
跨多个字段查询
对整个multi_match设置boost参数
curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/get-together/_search?pretty' -d '{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "elasticsearch big data",
"fields": ["name", "description"],
"boost": 2.5
}
}
}'
对multi_match中的特定字段设置boost参数,示例设置name字段的boost参数为3
curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/get-together/_search?pretty' -d '
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
//The name field being boosted by 3 with the ^ 3 suffix
"query": "elasticsearch big data",
"fields": ["name^3", "description"]
}
}
}'
在query_string中也可以单独设置term的boost参数值。示例如下:
curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/get-together/_search?pretty' -d '
{
"query": {
//Boosting a specific term by 3 with a ^3 suffix
"query_string": {
"query": "elasticsearch^3 AND \"big data\"
}
}
}'
注:对所有term设置boost参数和对所有term不设置boost参数效果是相同的
使用explain说明怎样给文档打分
示例:
curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/get-together/_search?pretty' -d '
{
"query": {
"match": {
"description": "elasticsearch"
}
},
"explain": true //Setting the explain flag in the request body
}'
//Result:
{
"hits": {
"total": 9,
"max_score": 0.4809364,
"hits": [{
"_shard": 0,
"_node": "Kwc3QxdsT7m23T_gb4l3pw",
"_index": "get-together",
"_type": "group",
"_id": "3",
"_score": 0.4809364,
"_source": {
"name": "Elasticsearch San Francisco",
"organizer": "Mik",
"description": "Elasticsearch group for ES users of all knowledge levels",
"created_on": "2012-08-07",
"tags": ["elasticsearch", "big data", "lucene", "open source"],
"members": ["Lee", "Igor"],
"location": "San Francisco, California, USA"
},
"_explanation": { //_explanation contains an explanation for the document’s score
"value": 0.4809364, //Top-level score for this document
"description": "weight(description:elasticsearch in 1) [PerFieldSimilarity], result of:", //Human- readable explanation for the score value
//Composite parts combined to make the final score
"details": [{
"value": 0.4809364,
"description": "fieldWeight in 1, product of:",
"details": [{
"value": 1.0,
"description": "tf(freq=1.0), with freq of:",
"details": [{
"value": 1.0,
"description": "termFreq=1.0"
}]
}, {
"value": 1.5389965,
"description": "idf(docFreq=6, maxDocs=12)"
}, {
"value": 0.3125,
"description": "fieldNorm(doc=1)"
}]
}]
}
}]
}
}
使用explain,优化调试query。
解释文档为什么没有匹配
示例:
curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/get-together/group/4/_explain' -d' {
"query": {
"match": {
"description": "elasticsearch"
}
}
}'
//Result:
{
"_id": "4",
"_index": "get-together",
"_type": "group",
"explanation": { //Explanation of why the document didn’t match the query
"description": "no matching term",
"value": 0.0
},
"matched": false //Flag indicating whether the document matched the query
}
使用explain API 可以详细获取特定文档与相应query的匹配情况。
重打分降低打分的干扰因素
应用场景之一就是优化性能。对大的结果集的前N个结果用新规则进行重新打分,以达到性能优化的目的
示例:
curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/get-together/_search?pretty' -d '{
//Original query to execute on all documents
"query": {
"match": {
"title": "elasticsearch"
}
},
"rescore": {
"window_size": 20, //Number of results on which to perform the rescore
"query": {
"rescore_query": {//Query that will run on the top 20 results of the original query
"match": {
"title": {
"type": "phrase",
"query": "elasticsearch hadoop",
"slop": 5
}
}
},
"query_weight": 0.8, //Weight of the scores from the original query
"rescore_query_weight": 1.3 //Weight of the scores from the rescored query
}
}
}'
自定义打分规则function_score
在Elasticsearch中function_score是用于处理文档score,它会在查询结束后对每一个匹配的文档进行一系列的重打分操作,最后以生成的最终分数进行排序。默认提供了几种的计算分值的函数
weight
weight的用法最为简单,只需要设置一个数字作为权重,文档的分数就会乘以该权重。
示例:
curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/get-together/_search?pretty' -d '
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"query": {
"match": {
"description": "elasticsearch"
}
},
"functions": [
//Boosting documents containing “hadoop” in the description by 2
{
"weight": 2,
"filter": { "term": { "description": "hadoop" } }
},
//Boosting documents containing “logstash” in the description by 3
{
"weight": 3,
"filter": { "term": { "description": "logstash" } }
}
]
}
}
}'
组合打分
score_mode: 指定各个函数分值之间的合并处理,可选参数:multiply, sum, avg, first, max, 或min。 默认为multiply。其中first表示采用第一个匹配的函数的分数
boost_mode: 指定计算后的分数与原始的score如何合并,可选参数:multiply,sum, avg, max, min, 或 replace。默认为multiply
field_value_factor
通过文档中某个字段的值计算出一个分数
- field:指定字段名其字段值为数值
- factor:对字段值进行预处理,乘以指定的数值(默认为1)
-
modifier:将字段值进行加工,有以下的几个选项:
- none:不处理(默认)
- log:计算对数
- log1p:先将字段值+1,再计算对数
- log2p:先将字段值+2,再计算对数
- ln:计算自然对数
- ln1p:先将字段值+1,再计算自然对数
- ln2p:先将字段值+2,再计算自然对数
- square:计算平方
- sqrt:计算平方根
- reciprocal:计算倒数
示例:按reviews字段值重新计算分数
curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/get-together/event/_search?pretty' -d '{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"query": {
"match": {
"description": "elasticsearch"
}
},
"functions": [
{
"field_value_factor": {
"field": "reviews", //Numeric field to use as a value
"factor": 2.5, //Factor the reviews field will be multiplied by
"modifier": "ln" //Optional modifier to calculate the score with
}
}
]
}
}
}'
Script
script支持我们自己编写一个脚本运行,在该脚本中我们可以拿到当前文档的所有字段信息,并且只需要将计算的分数作为返回值传回Elasticsearch即可。注:使用脚本需要首先在配置文件中打开相关功能
script.groovy.sandbox.enabled: true
script.inline: on
script.indexed: on
script.search: on
script.engine.groovy.inline.aggs: on
示例:提高category为电影院的文档的分值
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "天安门"
}
},
"script_score": {
"script": "return doc['category'].value == '电影院' ? 1.1 : 1.0"
}
}
}
}
优化:将脚本放在elasticsearch/config/scripts下,然后在查询语句中引用它:
category-score.groovy:
return doc['category'].value == '电影院' ? 1.1 : 1.0
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "天安门"
}
},
"script_score": {
"script": {
"file": "category-score"
}
}
}
}
}
进一步优化: 在script中还可以通过params属性向脚本传值,所以为了解除耦合,上面的DSL还能接着改写为:
category-score.groovy:
return doc['category'].value == recommend_category ? 1.1 : 1.0
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "天安门"
}
},
"script_score": {
"script": {
"file": "category-score",
"params": {
"recommend_category": "电影院"
}
}
}
}
}
}
但是,scripts 虽然强大但是性能不高(相较于内置的打分函数)
random
这个函数的使用相当简单,只需要调用一下就可以返回一个0到1的分数。它有一个非常有用的特性是可以通过seed属性设置一个随机种子,该函数保证在随机种子相同时返回值也相同,这点使得它可以轻松地实现对于用户的个性化推荐。
示例:
curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/get-together/event/_search?pretty' -d' {
"query": {
"function_score": {
"query": {
"match": {
"description": "elasticsearch"
}
},
"functions": [{
"random_score": {
"seed": 1234
}
}]
}
}
}'
decay functions (衰减函数)
衰减函数(Decay Function)提供了一个更为复杂的公式,它描述了这样一种情况:对于一个字段,它有一个理想的值,而字段实际的值越偏离这个理想值(无论是增大还是减小),就越不符合期望。这个函数可以很好的应用于数值、日期和地理位置类型,由以下属性组成:
- 原点(origin):该字段最理想的值,这个值可以得到满分(1.0)
- 偏移量(offset):与原点相差在偏移量之内的值也可以得到满分
- 衰减规模(scale):当值超出了原点到偏移量这段范围,它所得的分数就开始进行衰减了,衰减规模- 决定了这个分数衰减速度的快慢
- 衰减值(decay):该字段可以被接受的值(默认为0.5),相当于一个分界点,具体的效果与衰减的模式有关
衰减函数还可以指定三种不同的模式:线性函数(linear)、以e为底的指数函数(Exp)和高斯函数(gauss),它们拥有不同的衰减曲线
示例:希望租房的位置在40, 116坐标附近,5km以内是满意的距离,15km以内是可以接受的距离
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"query": {
"match": {
"title": "公寓"
}
},
"gauss": {
"location": {
"origin": { "lat": 40, "lon": 116 },
"offset": "5km",
"scale": "10km"
}
},
"boost_mode": "sum"
}
}
}
综合运用打分函数
在function_score中可以使用functions属性指定多个函数。它是一个数组,所以原有函数不需要发生改动。同时还可以通过score_mode指定各个函数分值之间的合并处理,boost_mode指定计算后的分数与原始的score如何合并。
示例1:向用户推荐一些不错的餐馆,特征是:范围要在当前位置的5km以内,有停车位是最重要的,有WIFI更好,餐厅的评分(1分到5分)越高越好,并且对不同用户最好展示不同的结果以增加随机性。
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"filter": {
"geo_distance": {
"distance": "5km",
"location": {
"lat": $lat,
"lon": $lng
}
}
},
"functions": [{
"filter": {
"term": {
"features": "wifi"
}
},
"weight": 1
}, {
"filter": {
"term": {
"features": "停车位"
}
},
"weight": 2
}, {
"field_value_factor": {
"field": "score",
"factor": 1.2
}
}, {
"random_score": {
"seed": "$id"
}
}],
"score_mode": "sum",
"boost_mode": "multiply"
}
}
}
这样一个饭馆的最高得分应该是2分(有停车位)+ 1分(有wifi)+ 6分(评分5分 * 1.2)+ 1分(随机评分)。
示例2:另一个例子是类似于新浪微博的社交网站。现在要优化搜索功能,使其以文本相关度排序为主,但是越新的微博会排在相对靠前的位置,点赞(忽略相同计算方式的转发和评论)数较高的微博也会排在较前面。如果这篇微博购买了推广并且是创建不到24小时(同时满足),它的位置会非常靠前。
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"query": {
"match": {
"content": "$text"
}
},
"functions": [{
"gauss": {
"createDate": {
"origin": "$now",
"scale": "6d",
"offset": "1d"
}
}
}, {
"field_value_factor": {
"field": "like_count",
"modifier": "log1p",
"factor": 0.1
}
}, {
"script_score": {
"script": "return doc['is_recommend'].value && doc['create_date'] > time ? 1.5 : 1.0",
params: {
"time": $time
}
}
}],
"boost_mode": "multiply"
}
}
}
白话计算公式:
_score * gauss(create_date, $now, "1d", "6d") * log(1 + 0.1 * like_count) * is_recommend&&is_in24 ? 1.5 : 1.0
使用script排序
搜索特定数据,利用相关数据排序。例如:搜索餐馆,主顺序根据点评数目排序,次级顺序采用原始分数。
{
"query": {
"match": {
"category": "餐馆"
}
},
"sort": [
{
"_script": {
"script": "doc['comments'].values.size()",
"type": "number",
"order": "desc"
}
},
"_score"
]
}
Field data cache (2.0以后启用Doc Values特性)
在有大量排序、数据聚合的应用场景,可以说field data cache是性能和稳定性的杀手。 对搜索结果做排序或者聚合操作,需要将倒排索引里的数据进行解析,然后进行一次倒排。这个过程非常耗费时间,因此ES 2.0以前的版本主要依赖这个cache缓存已经计算过的数据,提升性能。但是由于heap空间有限,当遇到用户对海量数据做计算的时候,就很容易导致heap吃紧,集群频繁GC,根本无法完成计算过程。 ES2.0以后,正式默认启用Doc Values特性(1.x需要手动更改mapping开启),将field data在indexing time构建在磁盘上,经过一系列优化,可以达到比之前采用field data cache机制更好的性能。因此需要限制对field data cache的使用,最好是完全不用,可以极大释放heap压力。
总结
- 利用TF和IDF计算文档的得分
- Elasticsearch 有许多工具自定义和修改文档的得分
- 对搜索子集重打分
- 使用explain API获取文档的得分细则
- 使用function_score自定义打分
- 了解新版Doc Values特性,优化大数据操作的性能
参考: http://www.scienjus.com/elasticsearch-function-score-query/ http://tech.boatingclouds.com/posts/2/view/15272 http://elasticsearch.cn/article/32