使用mapping定义文档的类型
逻辑上每个文档属于一个type,二而每个type属于一个index.indices就像关系型数据库,types就像表。
Types只是作为逻辑上的区分 Elasticsearch没有从物理上区分文档属于不同的type.所有文档从属于不区分type的相同index下,最终在物理上存放于相同shard的相同文集合里。
type是Elasticsearch的一个抽象概念,不是Lucene的。这个概念使得在逻辑上相同的index下可以有不同类型的文档。Elasticsearch负责维护这些文档。例如当你搜索时只过滤指定type的文档。
这导致了一个问题:在多个type中存在相同的字段名。为了避免不可预知的结果,同名的两个字段应该有相同的参数配置,否则Elasticsearch将消耗大量的计算资源寻找哪一个是正确的响应字段。这些字段都属于相同的Lucene index.例如group和event中都存在name字段,两个type中name字段都应该是string类型,不应该是一个string另一个是integer。这是现实中很少见的问题,但是还是值得参考以期避免不必要的麻烦
读取和定义mappings
读取MAPPING
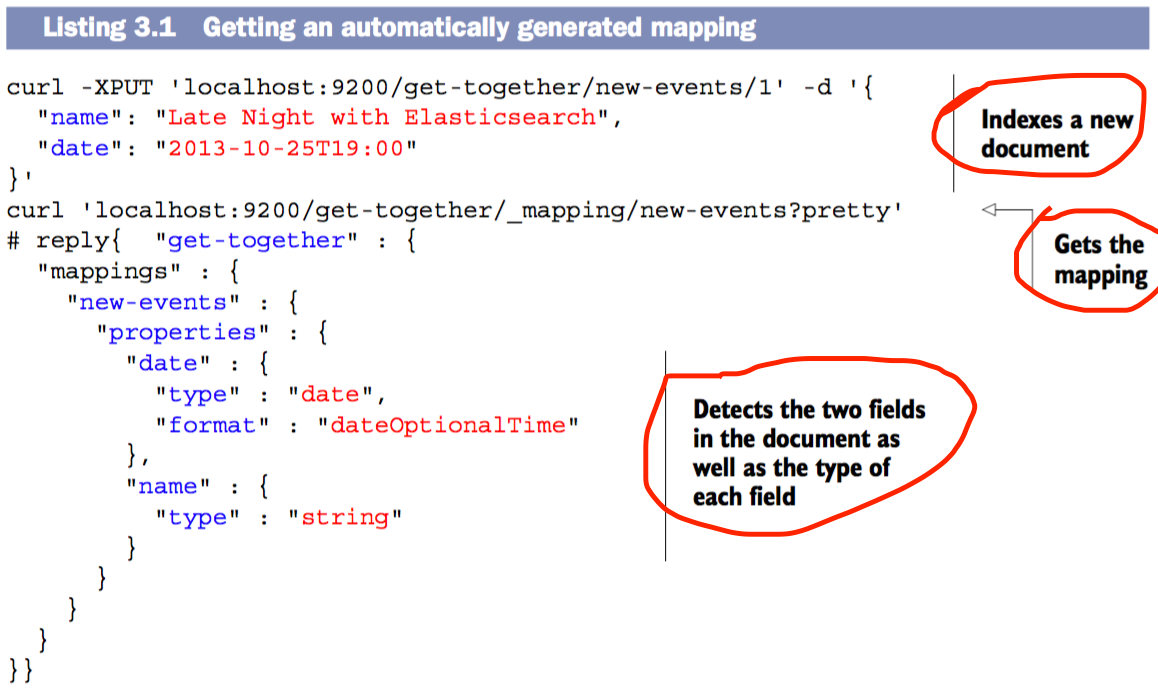
定义 MAPPING 定义mapping使用json字符串,例如下列示例定义string类型的host的字段
$ curl -XPUT 'localhost:9200/get-together/_mapping/new-events' -d '{
"new-events" : {
"properties" : {
"host": {
"type" : "string"
}
}
}
}'
当在空的type中创建index,将自动创建新的mapping
扩展已有的mapping
{
"get-together" : {
"mappings" : {
"new-events" : {
"properties" : {
"date" : {
"type" : "date",
"format" : "dateOptionalTime"
},
"host" : {
"type" : "string"
},
"name" : {
"type" : "string"
}
}
}
}
}
}
已有的mapping被新添加字段内型扩展Elasticsearch称之为合并已有的和新添加的mapping 不幸的是,并不是所有的合并都是成功的不能改变已有的字段类型,通常也不能改变已经index的字段类型。
修改mapping的唯一方法: 1. 从type中删除所有数据; 2. 创建新的mapping. 3. 重新索引数据.
定义文档字段的核心类型
Elasticsearch核心字段内型

String
String是最有趣的,因为有很多mapping选项以供分析使用;分析是转化分解文本并使得其与搜索相关的过程
term是来自于文本的单词,也是基本的搜索单元
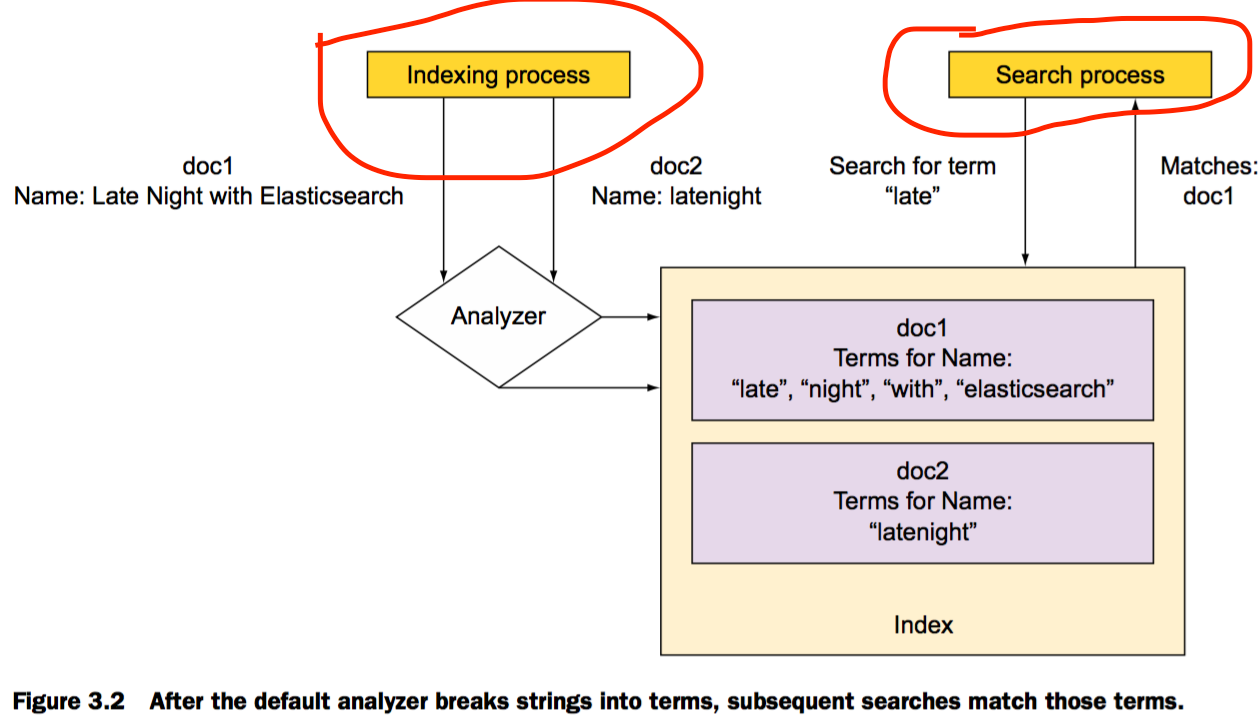
mapping字段属性index的可选值
字段属性index的可选值: analyzed (the default), not_analyzed, or no.
% curl -XPUT 'localhost:9200/get-together/_mapping/new-events' -d '{
"new-events" : {
"properties" : {
"name": {
"type" : "string",
"index" : "not_analyzed"
}
}
}
}'
- 设置字段的index属性值为
not_analyzed,那么字符串将被当做一个整体的索引关键词 - 设置字段的index属性值为
no,那么索引取消,该字段值也将不能被搜索
Numeric
Numeric类型即可以是short,integer,long,也可以是float,double.
Date
提供日期字符串,搜索文档。Elasticsearch会转化这些字符串使得其能在后台正常工作。原因是number比字符串处理的更高效和更快捷
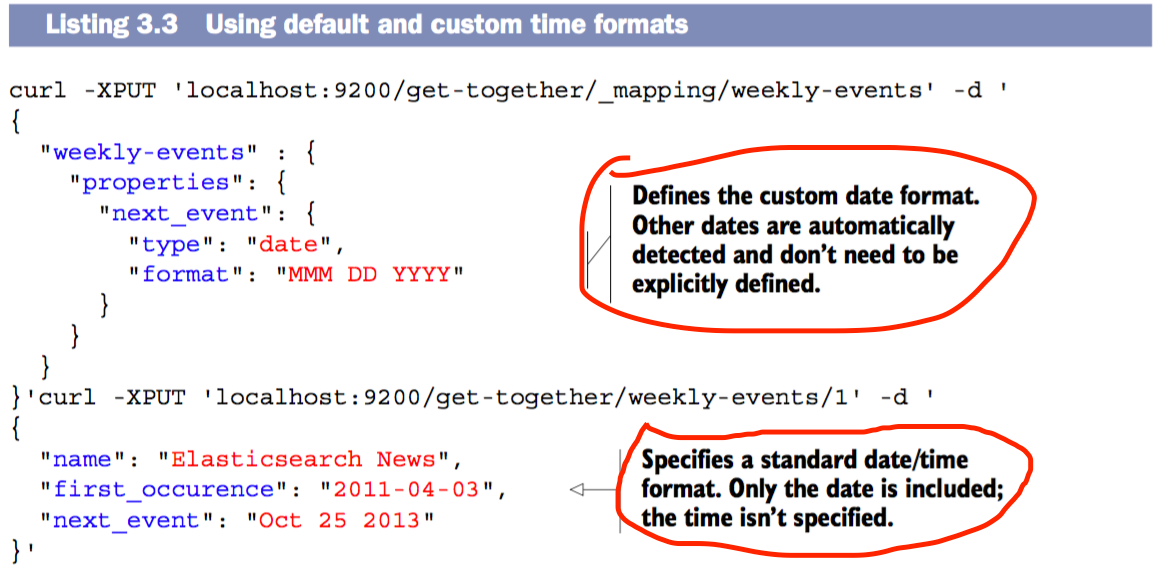
Boolean
boolean存储true/false值。在Luence中存储T代表true,F代表false.
数组字段和包含多字段的字段
数组字段
索引一个字段tags,其包含两个值。
$ curl -XPUT 'localhost:9200/blog/posts/1' -d '{
"tags": ["first", "initial"]
}'
读取tags的mapping
$ curl 'localhost:9200/blog/_mapping/posts?pretty'
#result
{
"blog" : {
"mappings" : {
"posts" : {
"properties" : {
"tags" : {
"type" : "string"
}
}
}
}
}
}
所有核心类型都支持array,使用单值和使用array一样不需要改变mapping.例如,另一篇博客只有一个tag,可以这样索引:% curl -XPUT 'localhost:9200/blog/posts/2' -d '{"tags": "second"}'
Multi-fields
配置posts type的字段tags,使其拥有两种不同的设置,一种是analyzed,匹配每个tag字;另一种是not_analyzed,只精确匹配tag全名
 搜索
搜索analyzed的tags,和一般的elasticsearch搜索是一样的。但是搜索not_analyzed时你需要指定全路径:tags.verbatim
将单值字段升级为多值字段不需要重新索引数据。但相反是行不通的,不能移除一个已经存在mapping的子字段
使用预定义字段
控制存储文档和搜索文档
_source存储原始内容- 返回源文档部分字段 设置存储选项为yes,可以存储独立的字段。尤其对于大文档是有用的,通常较大的数据集索引和搜索都比较慢
_all索引任何数据- 当你用
_all搜索时,Elasticsearch返回所有不做字段区分匹配结果 - 如果只需要搜索部分特定字段,也可以通过设置enabled为false关闭
_all的搜索匹配 - By default, each field is included in _all by having include_in_all implicitly set to true. You can use this option to control what is and isn’t included in _all
-
默认,每个字段都包含在
_all中,并且字段属性include_in_all被设置为true.也可以用这个选项控制哪些字段包含在_all中。例如下例$ curl -XPUT 'localhost:9200/get-together/_mapping/custom-all' -d '{ "custom-all": { "properties": { "organizer": { "type": "string", "include_in_all": false } } } }'如果没有指定搜索字段,Elasticsearch默认只匹配包含在
_all中的字段内容
- 当你用
标识文档
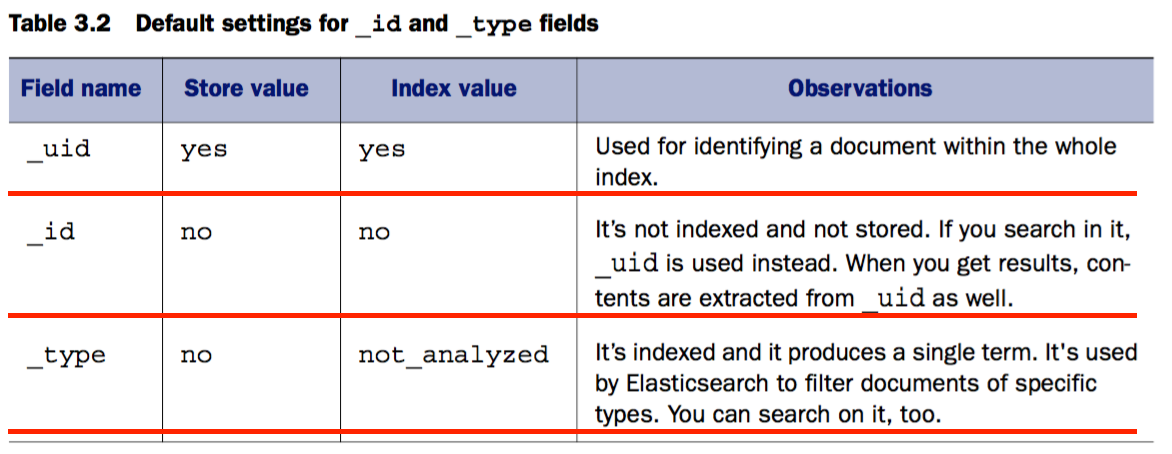
-
为即将索引的文档提供ID,如下例所示ID是
1st$ curl -XPUT 'localhost:9200/get-together/manual_id/1st?pretty' -d '{ "name": "Elasticsearch Denver" }' #reply { "_index" : "get-together", "_type" : "manual_id", "_id" : "1st", "_version" : 1, "created" : true } -
Elasticsearch自动生成ID
$ curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/logs/auto_id/?pretty' -d '{ "message": "I have an automatic id" }' #reply { "_index" : "logs", "_type" : "auto_id", "_id" : "RWdYVcU8Rjyy8sJPobVqDQ", "_version" : 1, "created" : true } -
在文档中存储index的名称
设置_index的enable属性为true,
$ curl -XPUT 'localhost:9200/get-together/_mapping/with_index' -d '{ "with_index": { "_index": { "enabled": true } } }'在该type下添加新的文档,重新运行搜索,应该返回新的包含index名称的文档。
更新已有文档
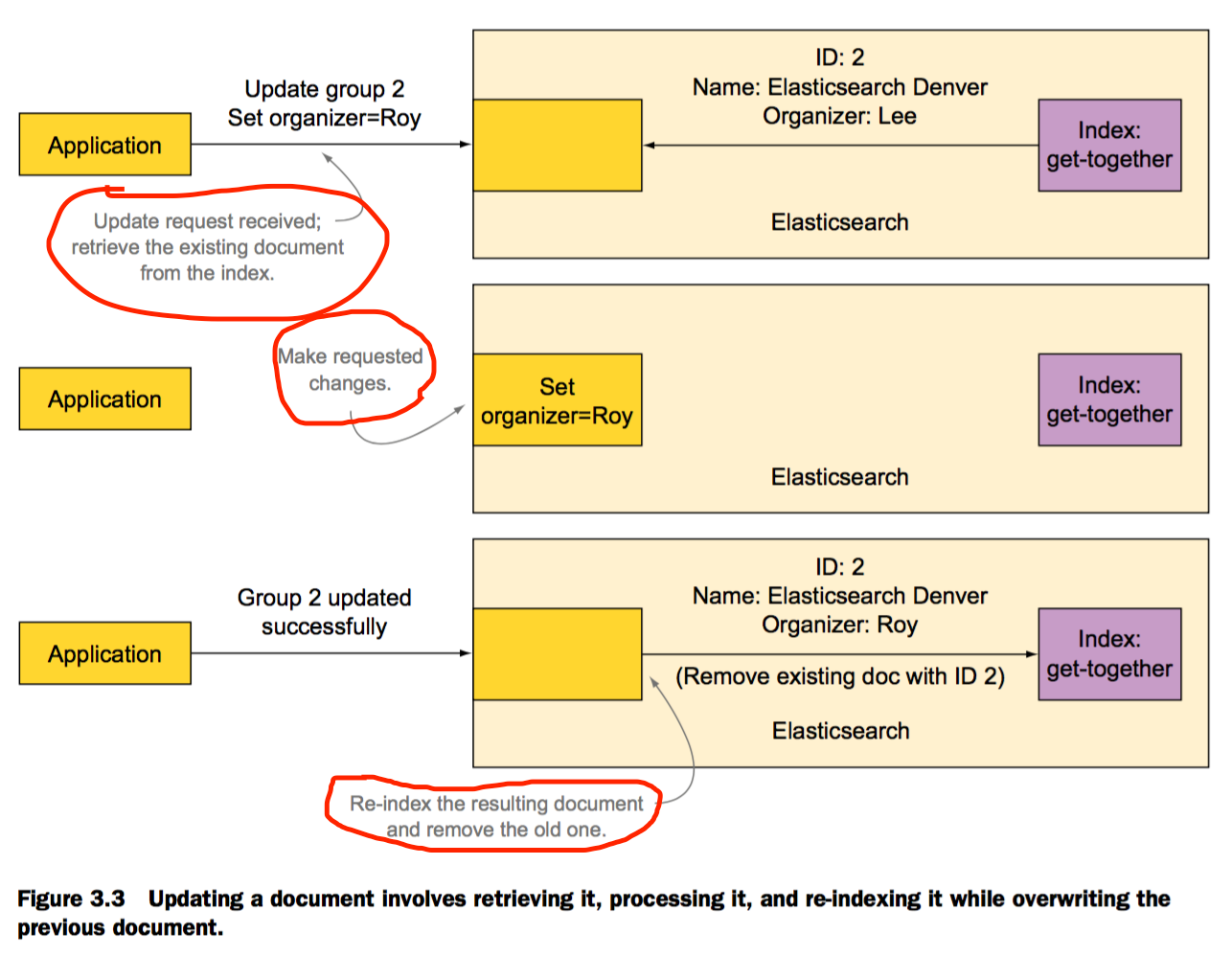
使用更新文档API
-
更新文档的部分内容 只需要发送需要更新的字段内容,即可实现部分更新。
-
采用upsert形式更新文档 更新的文档不存在,则使用初始值创建。
% curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/get-together/group/2/_update' -d ' { "doc": { "organizer": "Roy" }, "upsert": { "name" : "Elasticsearch Denver", "organizer": "Roy" } }' -
使用脚本更新文档
- Elasticsearch默认使用的脚本语言是Groovy.它的语法和java比较相识。
- 更新数据的过程:获取已有文档的_source,改变它,然后重新索引。脚本改变的是_source中的内容。这样
ctx._source引用_source,引用特定字段ctx._source.field_name - 如果需要使用变量,推荐将其定义在params参数中。原因是脚本需要编译,一次编译多次运行有利于提高性能
如下示例:使用Groovy脚本将price增加10
curl -XPUT 'localhost:9200/online-shop/shirts/1' -d ' { "caption": "Learning Elasticsearch", "price": 15 }' curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/online-shop/shirts/1/_update' -d '{ "script": "ctx._source.price += price_diff", "params": { "price_diff": 10 } }'
通过版本号实现并发
无法实现并发的示例
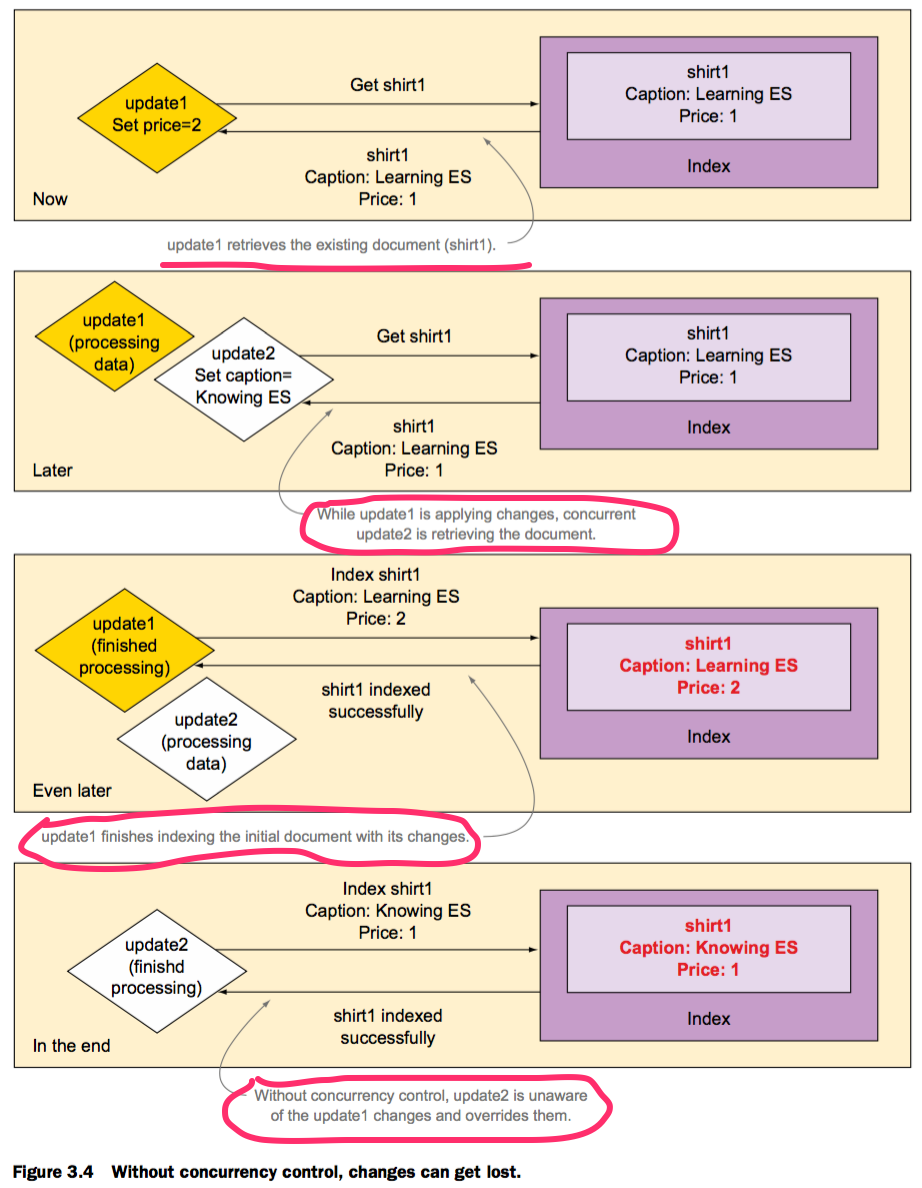
通过版本号实现并发
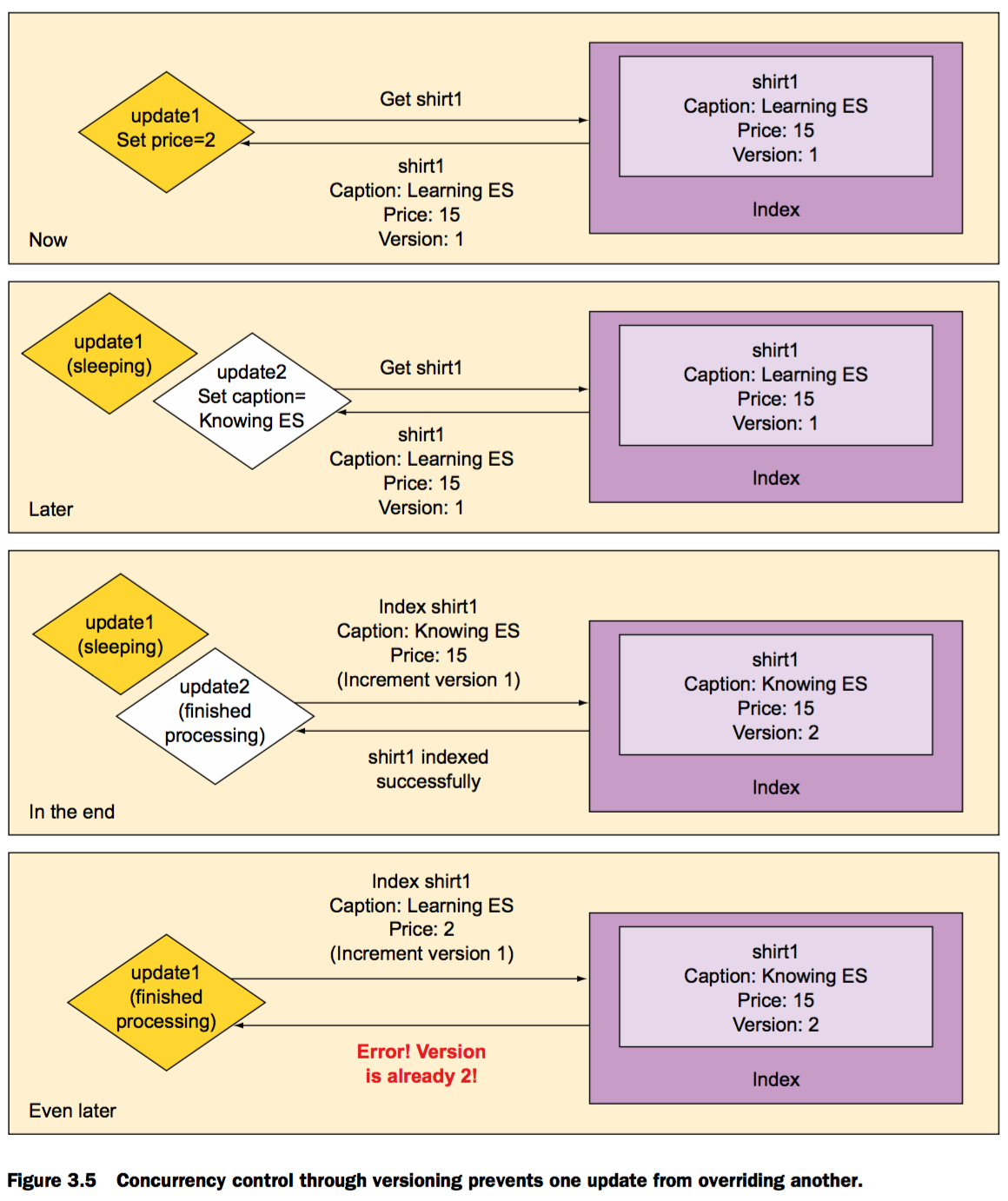
用版本控制并发更新,其中一个会更新失败

更新遇到冲突自动重试
$ SHIRTS="localhost:9200/online-shop/shirts"
$ curl -XPOST "$SHIRTS/1/_update?retry_on_conflict=3" -d '{
"script": "ctx._source.price = 2"
}'
索引文档时手动添加版本号
$ curl -XPUT 'localhost:9200/online-shop/shirts/1?version=3' -d '{
"caption": "I Know about Elasticsearch Versioning",
"price": 5
}'
使用外部版本号
依赖外部版本号,需要添加参数version_type=external在每次请求时
DOC_URL="localhost:9200/online-shop/shirts/1"
curl -XPUT "$DOC_URL?version=101&version_type=external" -d '{
"caption": "This time we use external versioning",
"price": 100
}'
这使得Elasticsearch可以接受任意数字版本号,只要比当前版本号大即可。但是不能自增版本号
删除数据
删除文档
-
删除单个文档
$ curl -XDELETE 'localhost:9200/online-shop/shirts/1' -
删除mapping type
$ curl -XDELETE 'localhost:9200/online-shop/shirts -
删除符合查询条件的文档
$ curl -XDELETE 'localhost:9200/get-together/_query?q=elasticsearch'
删除index
$ curl -XDELETE 'localhost:9200/get-together/'
删除多个index,index名称只需要用英文逗号分割即可。或者也可以使用
_all代替index名称,删除所有index。
注1:在elasticsearch.yml中配置action.destructive _requires_name: true禁止执行curl -DELETE localhost:9200/_all删除所有index。只有指定具体index名称才能删除index.
注2:删除index比删除文档快是因为。直接删除index是直接删除文件系统中的文件。删除文档只是标记为已删除,实际没有删除。只有到片段清理定时执行时才会删除。
关闭index
删除index的一个代替选项就是关闭index。当关闭一个index后,将不能对其进行读写,直到再次打开该index时。
通过POST请求接口_close关闭名为online-shop的index
$ curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/online-shop/_close'
通过POST请求接口_open打开名为online-shop的index
$ curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/online-shop/_open'